Industries and Climate Change
Pollution caused by Industries

Industrial pollution refers to the contamination of the environment by industrial activities. It occurs when harmful chemicals, waste materials, or byproducts of industrial processes are released into the air, water, or soil, causing damage to ecosystems, human health, and the environment. Industrial pollution can take various forms and arise from different sources within industries. Industrial facilities emit pollutants such as sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon monoxide (CO), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), particulate matter (PM), and hazardous air pollutants (HAPs) into the atmosphere. These pollutants can lead to smog formation, respiratory diseases, acid rain, and climate change.
Overview of the significant impact industries have on the Earth's climate:
- Industries consume fossil fuels for energy production and industrial operations, which is how they predominantly contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
- The climate is also impacted by other industrial processes like waste production, land use changes, and deforestation.
- Addressing the issues of global warming and supporting sustainable practices require an understanding of the relationship between industry and climate change.
How industrial pollution contributes to climate change:
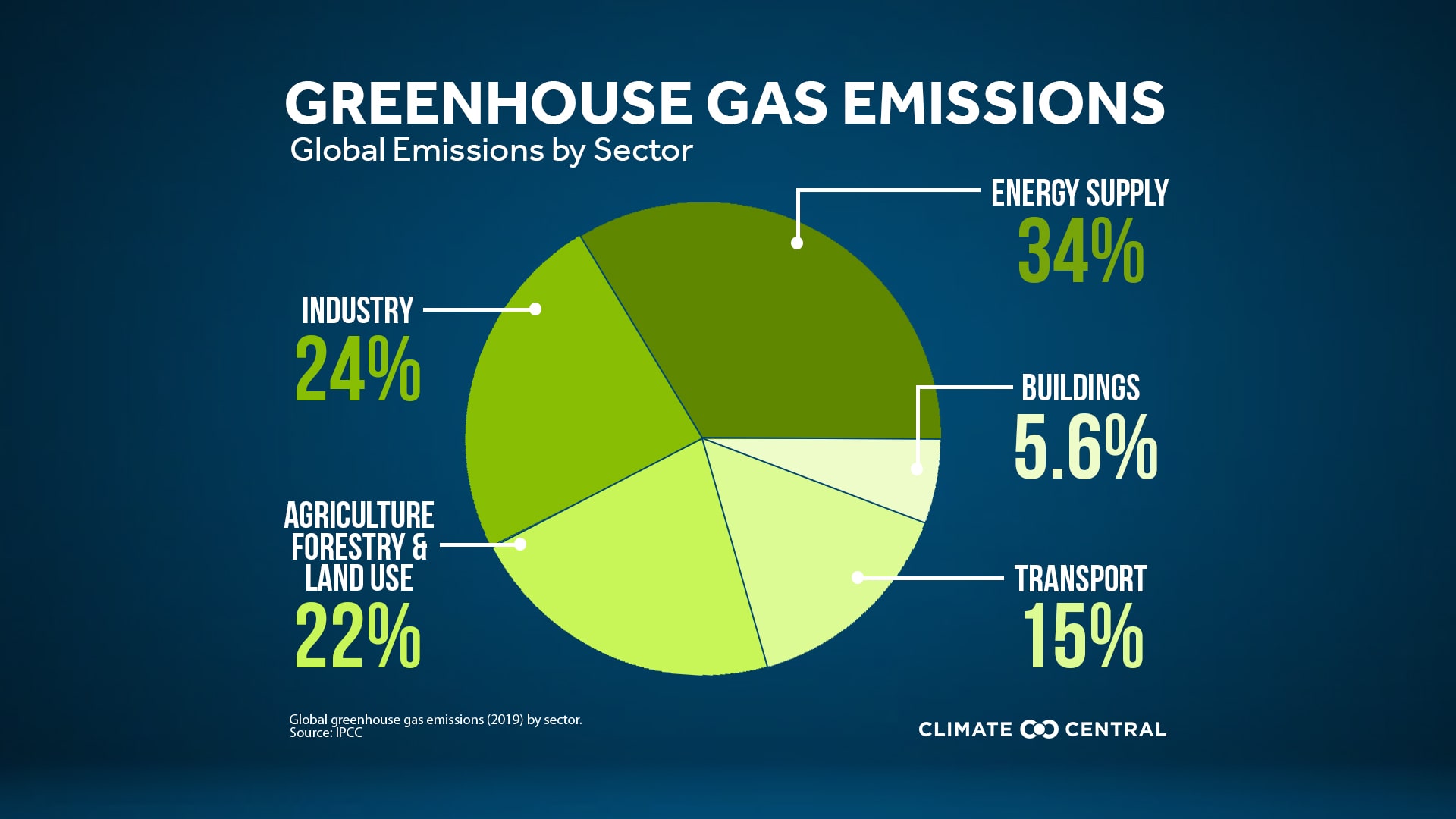
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions:Greenhouse gas emissions from industries are mostly caused by the burning of fossil fuels for energy production, manufacturing, and transportation. Industry-released carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and fluorinated gases trap heat in the atmosphere, causing climate change and global warming.
- Energy Production: Huge volumes of CO2 and other pollutants are released into the atmosphere during the combustion of fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas in power plants and other industrial facilities. This enhances the greenhouse effect, raising the Earth's average temperature and resulting in altered weather patterns, an increase in sea level, and other climatic effects.
- Industrial Processes: A number of industrial activities release greenhouse gases and other pollutants that
contribute to climate change, such as the manufacturing of chemicals, the smelting of metal, and the creation of
cement. For instance, the calcination of limestone during the cement-making process results in a considerable amount
of CO2 emissions, whereas the chemical
manufacturing process releases nitrous oxide and methane.

- Deforestation and Land Use Changes: Industries such as logging, agriculture, and urban development contribute to deforestation and land use changes, which release carbon stored in forests and soil into the atmosphere. Deforestation reduces the Earth's capacity to absorb CO2 and alters ecosystems, exacerbating climate change.
- Air Pollution: Industrial pollution not only emits greenhouse gases but also releases air pollutants such as sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These pollutants can affect the Earth's climate by influencing atmospheric composition, cloud formation, and regional climate patterns.
- Feedback mechanism:Climate change can be intensified by feedback mechanisms triggered by industrial pollutants. For instance, soot, or black carbon, released by industrial processes can accumulate on snow and ice surfaces, decreasing their albedo and hastening melting, both of which increase global warming and ice loss.
Summary
It will take coordinated action to cut emissions, advance energy efficiency, switch to renewable energy sources, and implement sustainable industrial practices in order to combat climate change brought on by industrial pollution. To mitigate the climatic impact of industrial operations and achieve climate goals, policy interventions, technological advances, and international cooperation are necessary.